Where Our Electricity Comes From
Aaron Wham • July 19, 2024
Electricity generation in the United States is a diverse and dynamic sector, employing a range of technologies and resources. This diversity ensures a reliable energy supply and allows for flexibility in addressing environmental and economic challenges. As of the latest data, the primary sources of electricity generation in the U.S. include natural gas, coal, nuclear power, renewable energy sources, and a small percentage from petroleum. Here is a detailed overview of each source and its contribution to the total electricity generation.
Natural Gas
Natural gas is the largest source of electricity in the U.S., accounting for about 40% of the total electricity generation. It is favored due to its abundance, relatively low cost, and lower carbon emissions compared to coal. Natural gas plants can be quickly ramped up or down, making them ideal for meeting fluctuating demand and complementing intermittent renewable sources like wind and solar.
Coal
Coal, once the dominant source of electricity in the U.S., has seen a significant decline over the past decade. It currently provides about 20% of the country's electricity. The decline is primarily due to the environmental regulations, the rise of natural gas, and the increasing competitiveness of renewable energy sources. Despite its reduction, coal remains a significant energy source, especially in regions with abundant coal resources.
Nuclear Power
Nuclear power contributes approximately 19% to the U.S. electricity mix. It is a reliable and low-carbon source of energy, providing baseload power that operates continuously to meet the constant demand. The U.S. has the largest fleet of nuclear reactors in the world, and while no new reactors have come online in recent years, existing plants have been upgraded and their operating licenses extended to maintain their contribution to the grid.
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources, including hydroelectric, wind, solar, biomass, and geothermal, collectively account for about 20% of electricity generation in the U.S.
Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power, which harnesses the energy of flowing water, contributes around 7% of the total electricity. It is a well-established and reliable renewable source, although its potential for expansion is limited due to environmental concerns and the scarcity of suitable sites for new dams.
Wind Power
Wind power has seen remarkable growth and now provides approximately 9% of the nation's electricity. Advances in technology have increased the efficiency and reduced the costs of wind turbines, making wind energy a competitive alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Solar Power
Solar power, though still a smaller portion of the energy mix, is rapidly expanding. It currently contributes about 3% of the total electricity generation. The decreasing cost of solar panels and supportive policies have spurred significant investment in both utility-scale solar farms and distributed solar installations on residential and commercial buildings.
Biomass and Geothermal
Biomass and geothermal energy together contribute around 1% of the electricity generation. Biomass energy comes from organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, and dedicated energy crops. Geothermal energy harnesses heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity. Both sources are valuable for their ability to provide consistent power, unlike some other renewable sources.
Petroleum
Petroleum is a minor player in electricity generation, accounting for less than 1% of the total. It is primarily used in areas where other resources are scarce or as a backup during peak demand periods.
In conclusion, the U.S. employs a diverse mix of energy sources for electricity generation, with natural gas leading the way, followed by coal, nuclear, and a growing share of renewables. This mix is continually evolving as economic, technological, and policy factors influence the energy landscape. The shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources is likely to continue, driven by environmental concerns and advances in technology.
If we can help you with any of your electricity needs, regardless of where it comes from, give us a call at 940-390-7606.

Energy Efficiency at Home: How Electrical Upgrades Can Lower Your Bills Electric bills in Texas can hit hard—especially during those blazing summers and unpredictable winters. But what if your electrical system could work smarter, not harder? With a few key upgrades, your home can run more efficiently and save you money month after month. At A and M Electrical Services, we help Texas homeowners make smart, energy-efficient upgrades that not only reduce utility costs but also increase home value and comfort. Let’s break down some of the best ways to cut down your energy bill with the power of electrical upgrades. 1. Switch to LED Lighting Still using incandescent or CFL bulbs? Switching to LED lighting throughout your home can slash your lighting energy use by up to 75% . LEDs also last years longer, meaning fewer replacements and less hassle. Bonus tip: Install dimmer switches and motion sensors to reduce unnecessary energy use in areas like hallways, closets, and bathrooms. 2. Upgrade Your Electrical Panel Older electrical panels can be inefficient, unsafe, and unable to handle the energy needs of modern appliances. Upgrading your panel not only improves efficiency but also protects your home from potential electrical hazards. If your panel is more than 25 years old, it might be time for an upgrade—especially if you've recently added new HVAC units, kitchen appliances, or a home EV charger. 3. Install Smart Thermostats and Outlets Smart devices help manage your energy use more effectively. A smart thermostat can adjust your heating and cooling based on your schedule, shaving off a chunk of your utility bill without you lifting a finger. Smart outlets allow you to turn off power to devices you aren’t using—like TVs, chargers, or computers that suck energy even when off. 4. Ceiling Fans and Whole-House Fans Well-placed ceiling fans help circulate air, meaning your HVAC system doesn’t have to work as hard. Installing or upgrading ceiling fans with efficient motors can add comfort and reduce cooling costs. Whole-house fans are another great option in milder months, pulling cool evening air through the house and pushing hot air out. 5. Surge Protection = Appliance Protection Texas weather can be unpredictable, and power surges can silently damage your electronics and appliances. Installing whole-home surge protection guards your home’s most expensive items—and helps them last longer. 6. Consider Solar Readiness Even if you’re not ready to go solar just yet, we can help make your home “solar ready.” That means installing the wiring, panels, or connections that make a future solar upgrade smoother—and often cheaper. Let’s Make Your Home Work Smarter Whether you’re looking to save money, increase safety, or reduce your home’s carbon footprint, energy-efficient electrical upgrades are a smart investment. At A and M Electrical Services, we’re proud to serve homeowners throughout North Texas with honest advice, expert work, and reliable service. Ready to upgrade? Let’s talk! 📞 Call us today at 940-390-7606 🔧 Locally owned. Family operated. Texas proud.

Keeping Cool and Powered Up: Electricity Tips for a Texas Summer Summer in Texas means long, sunny days, backyard BBQs, and—let’s be honest—higher electric bills. As temperatures rise, so does our reliance on electricity to keep our homes comfortable. Whether you’re cranking up the AC, running ceiling fans, or using extra appliances, summer is peak season for energy use. That makes it a great time to think about how your electrical system is holding up—and how to save a few bucks while staying safe and cool. Fun Fact: Did you know that air conditioning accounts for about 50% of the average Texas home’s summer electricity use? That’s more than cooking, lighting, and refrigeration combined. Here are a few smart summer electricity tips: Use Ceiling Fans Wisely – Fans don’t actually cool the air, but they do help your body feel cooler by moving the air around. Make sure your ceiling fans are set to rotate counterclockwise in the summer to push cool air downward. Schedule an Electrical Checkup – Summer storms and heavy usage can stress your electrical system. An inspection by a licensed electrician can catch worn outlets, overloaded circuits, or outdated panels before they become a problem. Keep Your AC Running Efficiently – Change filters regularly and consider upgrading your thermostat to a programmable or smart model. It can automatically adjust temperatures when you’re away, helping you save energy without lifting a finger. Also, wash those outside unit fins with a hose to remove the dust and dirt that has collected (turn off the breaker to the unit first!). Be Smart with Appliances – Try using heat-producing appliances like ovens and dryers in the early morning or evening. Better yet, grill outdoors and hang dry clothes when you can—it keeps the heat out of your house and saves electricity. As your local electrician, we're here to help make sure your home is summer-ready—from safety inspections to smart upgrades. Have questions or want to schedule a checkup? Give us a call at 940-390-7606 —we’d love to help you stay safe, comfortable, and energy-efficient this summer.

Storm season in Texas can be intense—between high winds, heavy rains, and plenty of lightning, your home's electrical system can take a serious hit. At A and M Electrical Services, we want to help you stay safe and avoid costly repairs by taking a few smart precautions before the storms roll in. Here’s what you need to know. 1. Install Whole-Home Surge Protection Power surges happen when there’s a sudden spike in voltage—often caused by lightning strikes or power line damage during storms. These surges can fry electronics, damage appliances, and even lead to electrical fires. Whole-home surge protectors are installed directly into your electrical panel to protect all your circuits. They act like a buffer between your home and outside voltage spikes. This is one of the best investments you can make to safeguard your electronics and appliances. 2. Check Your Grounding System Grounding is what keeps excess electricity from running wild in your system. A properly grounded electrical system channels extra voltage safely into the earth, reducing the risk of fire or shock. Over time, grounding rods can corrode or lose effectiveness, especially in the shifting Texas soil. Our team at A and M Electrical Services can inspect your system and ensure it's up to code and fully functional. 3. Using a Generator? Do It Safely Power outages are common during storm season. A backup generator can be a lifesaver, but only when used properly. Unsafe generator use can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning, backfeeding into power lines (which can be deadly for utility workers), or damaging your home’s electrical system. Tips for safe generator use: Never run a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces. Use a transfer switch—this ensures your generator powers your home safely without feeding electricity back into the grid. Have a licensed electrician install and inspect the setup. If you're considering a generator for your home, we can help with installation and make sure it’s wired safely and correctly. 4. Schedule a Pre-Storm Season Electrical Checkup The best time to protect your home is before the storms hit. At A and M Electrical Services, we offer electrical inspections that can identify vulnerabilities in your system—whether it’s outdated wiring, faulty breakers, or poor grounding. Stay Safe This Storm Season Your home is one of your biggest investments. Protecting it from electrical damage during storm season doesn’t have to be complicated—but it does take preparation. If you’d like a professional inspection, surge protection installation, or help setting up a generator, give A and M Electrical Services a call today at 940-390-7606 . We’re proud to serve our Texas neighbors with honest, reliable service you can count on—rain or shine.

The Hidden Risks of DIY Electrical Repairs – Why Calling a Licensed Pro Is the Smart Move With the rise of DIY tutorials and home improvement shows, it’s tempting to tackle electrical repairs yourself. After all, how hard can it be to swap out an outlet or fix a faulty light switch? The truth is, electrical work is one area where DIY can quickly turn dangerous. At A & M Electrical, we want to help homeowners understand the risks involved and why calling a licensed professional is always the best choice. 1. The Risk of Electrical Shock and Fire Electricity is unforgiving. Even a seemingly small mistake—like touching the wrong wire or miswiring a circuit—can result in serious injury or even death. According to the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI), thousands of people in the U.S. are injured each year due to electrical accidents. Additionally, improper electrical work is a leading cause of house fires . Hiring a licensed electrician ensures your home’s wiring is done safely and up to code, reducing these risks. 2. Code Violations and Insurance Issues Electrical work must meet strict local and national safety codes. A DIY repair may seem fine at first, but if it doesn’t comply with code, it could lead to costly problems down the road. Many insurance policies require that electrical work be done by a licensed professional. If an electrical fire occurs due to unpermitted or improper DIY work, your claim may be denied, leaving you responsible for expensive repairs. 3. Hidden Costs of DIY Mistakes What starts as a simple fix can quickly turn into a costly disaster. A wrong connection can damage appliances, overload circuits, or create hazards that aren’t immediately noticeable. Many homeowners end up calling a professional after a DIY attempt goes wrong, ultimately spending more money than if they had called an electrician from the start. 4. Time and Stress Let’s face it—electrical work isn’t just about knowing what wire goes where. It requires experience, troubleshooting skills, and specialized tools. What might take you hours (or days) to figure out, a trained electrician can fix safely and efficiently. Instead of spending your weekend watching tutorial videos and second-guessing your work, let the pros handle it while you enjoy peace of mind. 5. The A & M Electrical Advantage At A & M Electrical, our team of licensed and insured electricians brings expertise, safety, and reliability to every job. Whether it’s a simple outlet replacement, a full panel upgrade, or troubleshooting a tricky wiring issue, we ensure the job is done right the first time. We prioritize safety, efficiency, and compliance with all electrical codes, so you don’t have to worry. The Smart Move? Call a Licensed Electrician DIY has its place, but electrical work isn’t one of those areas where you should take risks. For the safety of your home and family, trust the experts. If you need electrical repairs or upgrades, contact A & M Electrical at 940-390-7606 today. We’ll provide professional, reliable service that keeps your home powered safely!

How to Safely Add Outdoor Lighting for Spring: A Step-by-Step Guide As the days get longer and the weather warms up, homeowners everywhere are eager to enjoy their outdoor spaces. Adding outdoor lighting is a great way to enhance your garden, patio, or walkway—while also improving safety and curb appeal. However, improper installation can lead to electrical hazards, so it's crucial to take the right precautions. Follow this step-by-step guide to brighten your yard without risk. Step 1: Plan Your Lighting Layout Before purchasing any lights, decide where and how you want to illuminate your space. Consider these key areas: Pathways & Walkways – Ensure safe footing by lining paths with stake lights. Patios & Decks – Use string lights or wall-mounted fixtures for ambiance. Garden Features – Highlight trees, flower beds, or fountains with spotlights. Home Perimeter – Increase security with motion-sensor floodlights. Sketch out a simple layout, noting the locations of power sources and any potential obstacles. Step 2: Choose the Right Type of Outdoor Lighting Outdoor lighting comes in various forms, and selecting the right type is essential for safety and efficiency: Solar-Powered Lights – Easy to install and energy-efficient, requiring no wiring. Low-Voltage Lights – Safer than standard 120V systems, requiring a transformer to reduce voltage. LED Fixtures – Long-lasting, cost-effective, and available in many styles. Smart Lights – Can be controlled remotely via apps or voice assistants for convenience. Step 3: Use Weatherproof Components Since outdoor lighting is exposed to the elements, always choose fixtures rated for outdoor use. Look for: Waterproof Casing – Ensure all lights and electrical connections have appropriate weatherproof seals. Outdoor-Rated Cables – Avoid standard indoor extension cords, as they aren’t designed to handle moisture and temperature changes. GFCI Outlets – Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI) are essential for preventing electrical shock when plugging in outdoor lights. Step 4: Follow Safe Installation Practices When installing outdoor lighting, keep these safety tips in mind: Turn Off Power – Always cut the power at the breaker before working with electrical components. Bury Cables Properly – If using wired lights, bury cables at least 6 inches underground and use protective conduit to prevent damage. Avoid Overloading Circuits – Check your electrical capacity to prevent short circuits or blown fuses. Secure Fixtures Well – Mount lights securely to avoid wind damage or accidental disconnections. Step 5: Test and Adjust Once installed, test your lighting system at dusk to see if it provides the desired effect. Make adjustments to angles and placement as needed. If using solar lights, ensure they receive adequate sunlight during the day to charge effectively. Step 6: Maintain Your Outdoor Lighting To keep your lighting system safe and functional: Check for Exposed Wires – Inspect cables periodically for wear and tear. Clean Fixtures – Remove dirt, debris, and insects to maintain brightness. Replace Bulbs as Needed – Swap out dim or flickering bulbs to keep your space well-lit. Brighten Your Outdoor Space with Confidence With the right approach, outdoor lighting can transform your yard into a welcoming retreat while ensuring safety for you and your guests. By following these simple steps, you’ll enjoy a beautifully illuminated outdoor space just in time for spring. Need professional advice? Call us today at 940-390-7606 for more complex installations or if you have any doubts about your setup. Happy lighting!
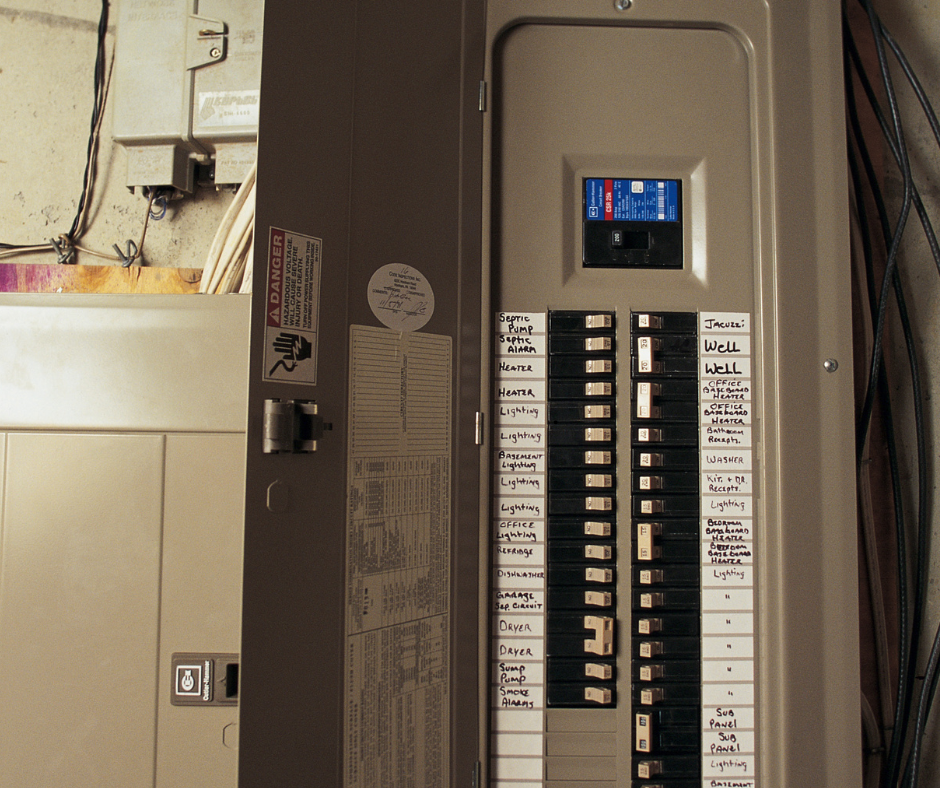

Understanding Your Home's Electrical Panel: What Every Homeowner Should Know Your home’s electrical panel is the heart of your electrical system. It’s what keeps your lights on, your appliances running, and your home safe. But for many homeowners, it’s a bit of a mystery box. Understanding how it works—and when it needs attention—can save you time, money, and potential hazards down the road. What Is an Electrical Panel? Your electrical panel, also called a breaker box, is the hub where electricity from your utility company enters your home and is distributed to different circuits. Inside, you’ll find a series of circuit breakers that act as safety devices. When a circuit gets overloaded, the breaker trips, cutting power to prevent overheating and potential fires. Signs Your Panel Needs Attention Not all electrical panels are created equal, and like anything in your home, they can wear out over time. Here are some common signs that you may need an upgrade or repairs: Frequent breaker trips – If your breakers keep tripping, your system may be overloaded. Buzzing or humming sounds – This could indicate a faulty breaker or a loose connection. Burn marks or a burning smell – These are major red flags and should be addressed immediately. Your home still has fuses – If your home has an old fuse box instead of a modern breaker panel, it’s time for an upgrade. You’re planning renovations or adding major appliances – More power-hungry appliances mean more demand on your panel. Why It’s Important to Keep Your Panel Updated An outdated or malfunctioning panel isn’t just inconvenient—it’s a safety risk. Overloaded circuits can lead to electrical fires, and old panels may not provide enough power for modern household needs. Keeping your panel in good shape ensures your home runs efficiently and safely. Call the Experts at A & M Electrical Services Not sure about the state of your electrical panel? Don’t take risks when it comes to your home’s electrical system. At A & M Electrical Services , we specialize in panel inspections, upgrades, and repairs to keep your home powered safely. Give us a call today at 940-390-7606 and let’s make sure your electrical system is in top shape!

Why You Should Upgrade to LED Lighting: Savings, Safety, and Style Upgrading to LED lighting is one of the smartest investments a homeowner can make. Whether you're looking to lower energy bills, enhance your home's safety, or modernize your interior design, LED lighting offers numerous benefits. Here’s why making the switch is a bright idea. Savings That Shine LED bulbs consume up to 80% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, significantly reducing electricity costs. While the initial investment in LED bulbs may be slightly higher, their long lifespan—often 15 to 25 times longer than incandescent options—means fewer replacements and greater savings in the long run. Additionally, many utility companies offer rebates and incentives for switching to energy-efficient lighting, making the transition even more cost-effective. Enhanced Safety for Your Home LED lighting is a safer alternative compared to traditional bulbs. Incandescent and halogen bulbs generate excessive heat, increasing the risk of fire hazards. In contrast, LEDs produce minimal heat , reducing the chances of overheating or accidental burns. Furthermore, LED bulbs contain no toxic materials, such as mercury, making them an environmentally friendly and health-conscious choice for your home. Stylish and Versatile Designs Modern LED lighting solutions offer a wide range of design possibilities. From sleek recessed lighting to ambient smart bulbs that change c o l o r with a simple app command, LEDs allow homeowners to customize their lighting to suit any mood or occasion. Whether you’re looking to create a warm, inviting atmosphere in your living room or enhance task lighting in the kitchen, LED technology provides flexible and stylish options for every space. Smart Home Integration Many LED lighting systems are compatible with smart home technology, allowing you to control brightness, color, and schedules with voice commands or mobile apps. This added convenience helps improve energy efficiency while providing seamless control over your home’s ambiance. Make the Switch Today Switching to LED lighting is an easy and effective way to improve your home’s efficiency, safety, and style. With energy savings, reduced maintenance, and countless design possibilities, there’s no reason to delay the upgrade. Start transforming your home with LED lighting today and enjoy a brighter, smarter future! If we can help you make the switch to LED, or if you have any other electrical need, give us a call at 940-390-7606 .

5 Common Electrical Issues in Older Homes and How to Fix Them If you live in an older home, you might love its charm and character—but the electrical system? Not so much. Outdated wiring and old electrical panels can lead to safety hazards and everyday frustrations. Here are five common electrical issues in older homes and how to fix them. 1. Outdated Wiring Many older homes still have knob-and-tube or aluminum wiring, which can be a fire hazard. These systems weren’t designed to handle today’s electrical loads. If your home has outdated wiring, consider hiring an electrician to replace it with modern copper wiring. This is a significant investment, but it’s crucial for safety and can increase your home’s value. 2. Frequent Tripping Breakers If your breakers trip often, your electrical panel might be overloaded. Older homes weren’t built with modern appliances in mind, and their panels often can’t handle today’s power demands. Upgrading to a 200-amp panel can resolve this issue and prevent future power disruptions. 3. Ungrounded Outlets Two-prong outlets are common in older homes, but they lack the grounding needed to protect your devices from power surges. The best fix is to have an electrician install grounded three-prong outlets. If rewiring isn’t an option, a GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlet can offer some protection. 4. Flickering or Dimming Lights Do your lights flicker when you turn on a high-powered appliance? This could be due to outdated wiring, loose connections, or an overloaded circuit. A licensed electrician can diagnose the cause and either tighten connections, add dedicated circuits, or upgrade wiring to ensure steady power. 5. Overloaded or Damaged Outlets Older homes often lack enough outlets, leading homeowners to rely on extension cords and power strips, which can be a fire risk. If you see scorch marks on outlets or experience frequent plug failures, it’s time to add more outlets. A professional can install additional circuits to safely distribute power. Final Thoughts While these electrical issues are common in older homes, they’re not something to ignore. A licensed electrician can help bring your home’s electrical system up to modern safety standards. Investing in electrical upgrades not only improves safety but also enhances convenience and increases your home’s value. If you need any advice or help updating your system, give us a call today at 940-390-7606 .

Spring Electrical Checklist: Get Your Home Ready for Warmer Days As winter fades and spring rolls in, it's the perfect time to give your home's electrical system a little attention. With more daylight, changing temperatures, and an increase in outdoor activities, your electrical setup should be ready to handle the transition. Here are a few easy things you can do to make sure everything is running smoothly. 1. Check Your Outdoor Outlets & Lighting Winter can be rough on outdoor outlets and lighting. Snow, ice, and freezing temps may have caused damage, so take a few minutes to inspect them. Look for cracked covers, loose connections, or signs of wear. If you have outdoor lighting for patios, walkways, or landscaping, make sure all the bulbs are working and replace any that aren’t. 2. Inspect Your Surge Protectors With spring storms on the horizon, it’s a good idea to check your surge protectors. If you’re relying on power strips that don’t offer real surge protection, now’s the time to upgrade. Whole-home surge protectors are a great investment to keep your appliances and electronics safe from unexpected power surges. 3. Test Your GFCI Outlets Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlets are required in areas like kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor spaces to prevent electric shocks. Test them by pressing the "test" button—if the power cuts off and resets properly, you're good to go. If not, it might be time for a replacement. 4. Give Your HVAC System Some Electrical Love Your heating system is getting a break, but your air conditioning is about to take center stage. Make sure your AC unit is ready by checking the circuit breaker, replacing the air filter, and ensuring the outdoor condenser unit is clear of debris. If anything seems off, an HVAC technician can help before the heat kicks in. 5. Clean and Check Ceiling Fans Dust those ceiling fan blades and switch them to spin counterclockwise. This pushes cool air down, helping your home stay comfortable as temperatures rise without overworking your AC. 6. Look for Overloaded Circuits With holiday lights and space heaters put away, now’s a good time to evaluate whether any circuits were overloaded. If you tripped breakers frequently in the winter, consider redistributing your electronics or talking to an electrician about adding circuits. Taking a little time now can prevent bigger electrical headaches later in the season. A few simple checks will help your home stay safe, efficient, and ready for all the fun that spring brings! We are always here to help you with all of your electrical needs. Just give us a call at 940-390-7606 !
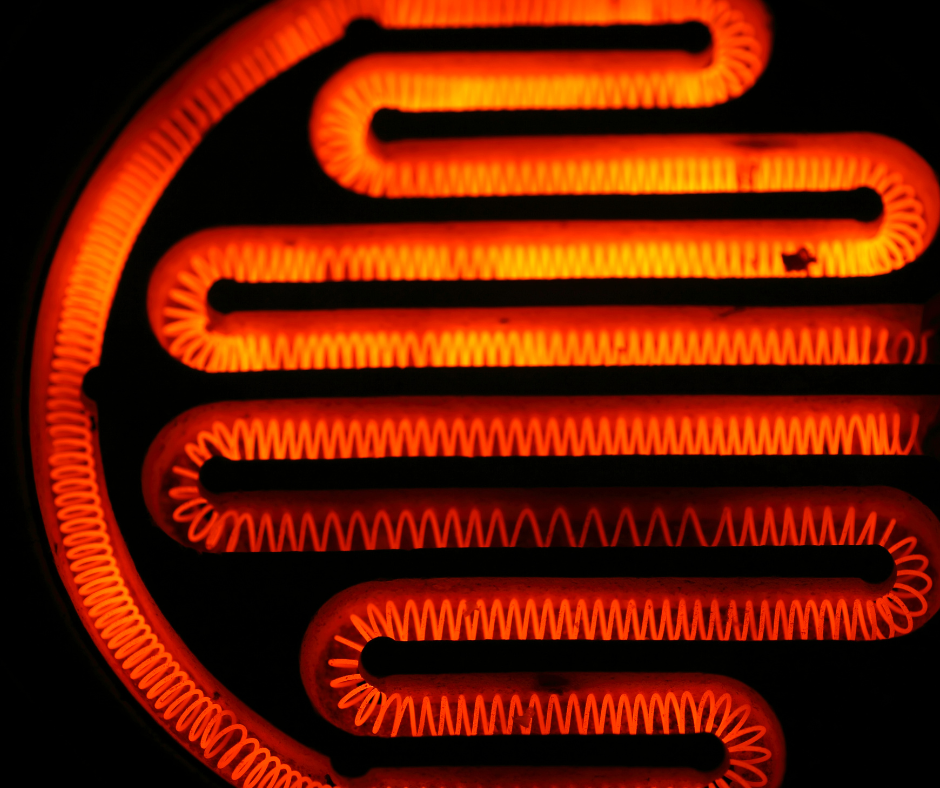
Why Do Appliances with Heating Elements Use So Much Electricity? Ever notice how your electric bill seems to spike in the winter when you're using space heaters or when you're baking up a storm during the holidays? That’s because appliances with heating elements—things like ovens, toasters, hair dryers, and space heaters—pull a lot more electricity than other household items. But why? Why Heating Appliances Are Power Hogs The key reason is simple: heat requires energy. Heating elements convert electricity into heat using resistance, meaning the appliance has to draw a lot of power to generate enough warmth. Compare that to something like a TV or LED light, which only need a small amount of electricity to function. For example, a standard lightbulb might use 10–15 watts, but a space heater can easily pull 1,500 watts or more . That’s a huge difference! The Dangers of Overloading a Circuit Most household circuits are designed to handle a certain amount of electrical load, typically 15 or 20 amps. If you plug in multiple high-wattage appliances on the same circuit—like a space heater and a microwave—you could overload the circuit. When that happens, your breaker trips, cutting power to prevent overheating and potential electrical fires. But sometimes, warning signs appear before the breaker trips. If you notice: - Flickering lights when an appliance turns on - Warm or buzzing outlets - Frequently tripping breakers …it’s time to rethink what’s plugged in where. How to Check an Appliance’s Power Draw Every appliance has a label (usually on the back or bottom) listing its amperage (A) or wattage (W). To find out how many amps an appliance pulls, use this simple formula: Amps = Watts ÷ Volts Most U.S. homes run on 120-volt circuits, so if your space heater is 1,500 watts: 1,500W ÷ 120V = 12.5A That means just one space heater could use most of a 15-amp circuit’s capacity—leaving little room for anything else. Bottom Line If your home has frequent breaker trips or warm outlets, be mindful of how many high-wattage appliances are running at the same time. Checking the amp draw of your devices can help prevent overloads and keep your home safe. When in doubt, spread out your appliances across multiple circuits or consider upgrading older wiring with the help of an electrician. Stay safe and warm—without overloading your home’s electrical system! If you have any questions or need help with your electrical system in any way, give us a call at 940-390-7606 today!
